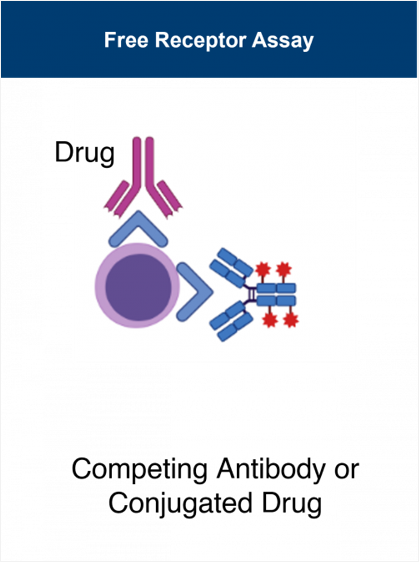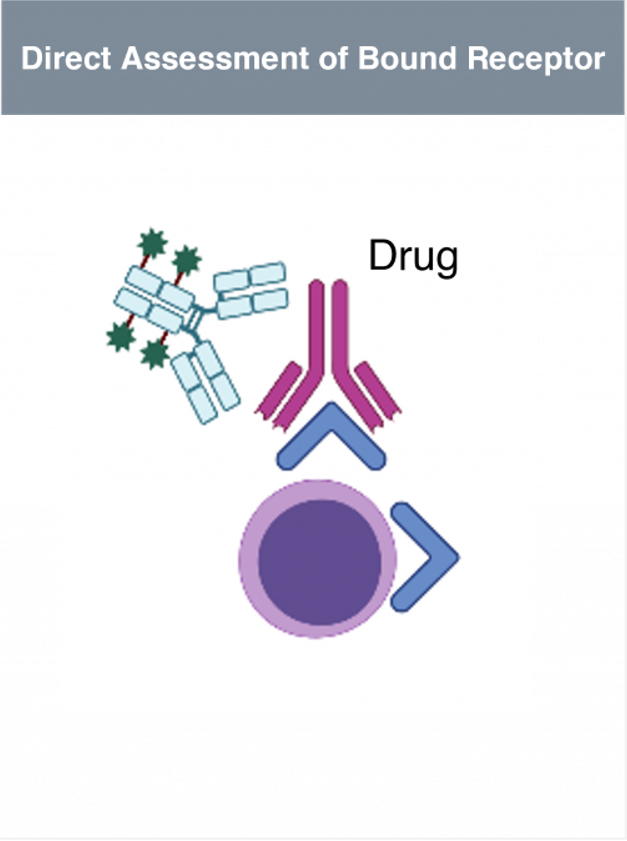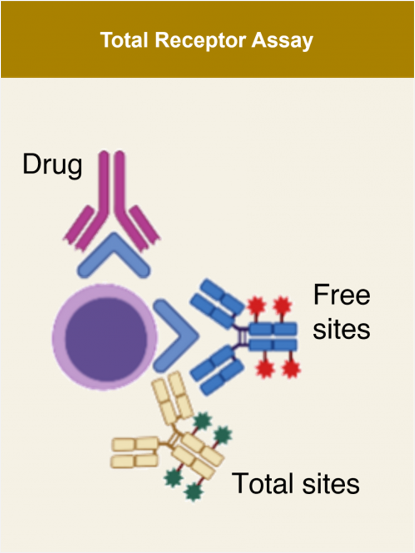
Translational Research - Lab Services
The Immune System's Secret Language: Unlocking Cellular Communication
|
-

Rob Maiale
has not third author: true, (SizeLimitingPyMap: {main={hs_id=159488778858, hs_child_table_id=0, hs_updated_at=1754641583843, hs_published_at=1768210872876, description=Rob Maiale is a marketing strategist and creative technologist with 17 years of experience turning complex ideas into growth. He currently leads content strategy, where he transforms insights from Precision experts into market-shaping narratives that drive the advancement of next-generation therapies. Rob’s career spans journalism, advertising, and brand storytelling, with a through-line of making the meaningful memorable. His work blends creative strategy with emerging AI tools to help Precision stay ahead of the curve—and above the noise., avatar=Image{width=287,height=287,url='https://5014803.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/5014803/PfM%20Website/PfMxMarkentive/authors/rob.png',altText='rob',fileId=194099000843}, linkedin=https://www.linkedin.com/in/rob-maiale/, hs_name=, hs_path=, lastname=Maiale, hs_initial_published_at=1767768596569, hs_created_at=1709645745089, hs_is_edited=false, hs_deleted_at=0, name=Rob, position=Associate Director, Digital Content & Inbound Marketing, job=, slug=rob-maiale, email=, hs_updated_by_user_id=65160865}, second={}, third={}})